SMT Line: The Backbone of PCBA Manufacturing
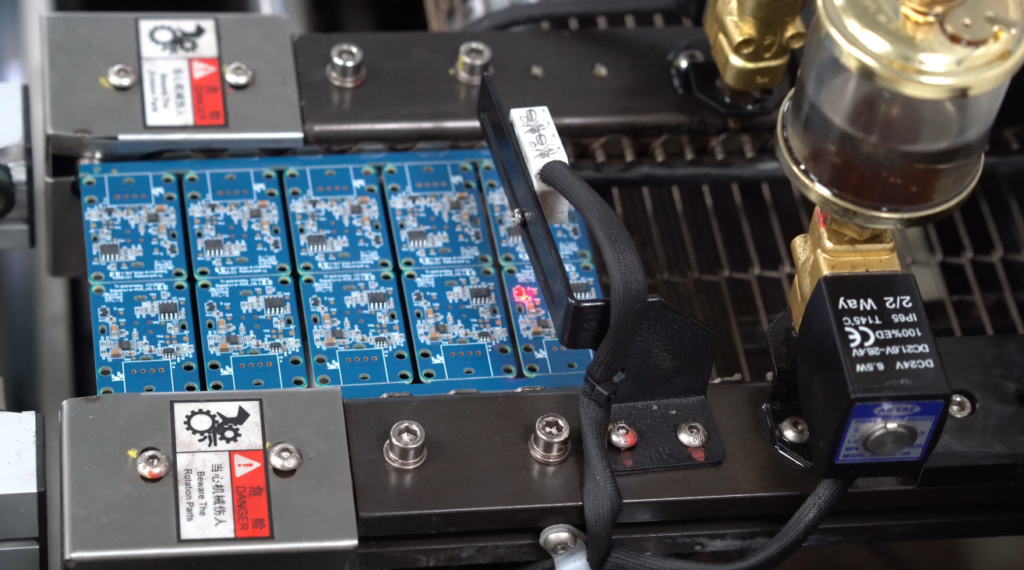
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) lines are at the heart of modern Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) manufacturing. With the increasing demand for high-density, miniaturized, and complex PCBs in industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, and telecommunications, efficient and reliable SMT lines have become essential for delivering high-quality products.
This article explores the components, workflow, and advantages of an SMT line, shedding light on its critical role in the PCBA industry.
What is an SMT Line?
An SMT line refers to a series of automated equipment used to assemble electronic components onto a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) using Surface Mount Technology. Unlike through-hole assembly, SMT mounts components directly onto the surface of the PCB, enabling higher component density and faster production.
Key Components of an SMT Line
A typical SMT line consists of the following core equipment:
- Stencil Printer:
- Applies solder paste to the PCB pads using a stencil.
- Ensures precise and even distribution for strong component connections.
- SPI (Solder Paste Inspection):
- Inspects the applied solder paste for volume, alignment, and thickness.
- Prevents defects early in the process.
- Pick-and-Place Machine:
- Automatically places surface-mount components onto the solder-pasted PCB.
- Handles components with high precision at incredible speeds.
- Reflow Oven:
- Heats the PCB to melt the solder paste, forming reliable joints between components and pads.
- Employs controlled temperature profiles to prevent damage to sensitive components.
- AOI (Automated Optical Inspection):
- Uses cameras to inspect solder joints, component placement, and polarity.
- Identifies assembly defects before moving to the next stage.
- Conveyor System:
- Connects the equipment in the SMT line, enabling smooth movement of PCBs.
- Ensures seamless transitions between stages.
- ICT (In-Circuit Testing) and Functional Testing (optional):
- Checks the electrical functionality and connectivity of the assembled PCB.
- Ensures the board meets design specifications.
Workflow of an SMT Line
- Solder Paste Printing: The process begins with the stencil printer applying solder paste to the PCB.
- Component Placement: The pick-and-place machine mounts components with extreme accuracy.
- Reflow Soldering: The PCB passes through a reflow oven, where the solder paste melts and solidifies, creating strong electrical and mechanical bonds.
- Inspection:
- SPI and AOI systems identify defects such as solder paste misalignment, component shifts, or poor solder joints.
- Defective boards can be repaired or rejected at this stage.
- Testing: Functional testing ensures the PCB operates as intended, validating the integrity of the assembly process.
Advantages of an SMT Line in PCBA Manufacturing
- High Precision and Accuracy: SMT lines can place even the smallest components, such as 0201 or 01005 packages, with exceptional accuracy.
- Increased Efficiency: Automated SMT lines significantly reduce assembly time, enabling high-volume production with consistent quality.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Automation reduces labor costs and minimizes errors, leading to lower production costs in the long run.
- Scalability: SMT lines are highly flexible and capable of handling both small-batch prototyping and large-scale production.
- Compact Designs: Enables the production of compact, lightweight PCBs with high component density, meeting modern industry demands.
- Enhanced Reliability: SMT assembly produces stronger solder joints and better electrical performance, ensuring long-term reliability.
Challenges in SMT Line Operations
While SMT lines offer numerous benefits, they also come with challenges:
- High Initial Investment: Setting up an SMT line requires significant capital for advanced equipment.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is crucial to avoid downtime and ensure precision.
- Skilled Operators: Skilled personnel are needed to program and manage the line effectively.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent quality across batches requires robust inspection and testing processes.
Best Practices for Managing SMT Lines
To maximize efficiency and quality, PCBA manufacturers should follow these best practices:
- Optimize Production Parameters: Regularly adjust reflow profiles and placement settings for different PCB designs.
- Implement Process Monitoring: Use real-time monitoring systems to detect and correct issues during assembly.
- Invest in Training: Train operators and technicians to manage and troubleshoot SMT equipment effectively.
- Perform Routine Maintenance: Schedule regular equipment maintenance to prevent unplanned downtime.
Conclusion
SMT lines are the backbone of PCBA manufacturing, enabling the production of complex, high-quality, and reliable electronic assemblies. With their advanced automation, precision, and efficiency, SMT lines empower manufacturers to meet the growing demands of various industries. By investing in cutting-edge SMT technology and adhering to best practices, PCBA manufacturers can deliver superior products and maintain a competitive edge in the market.